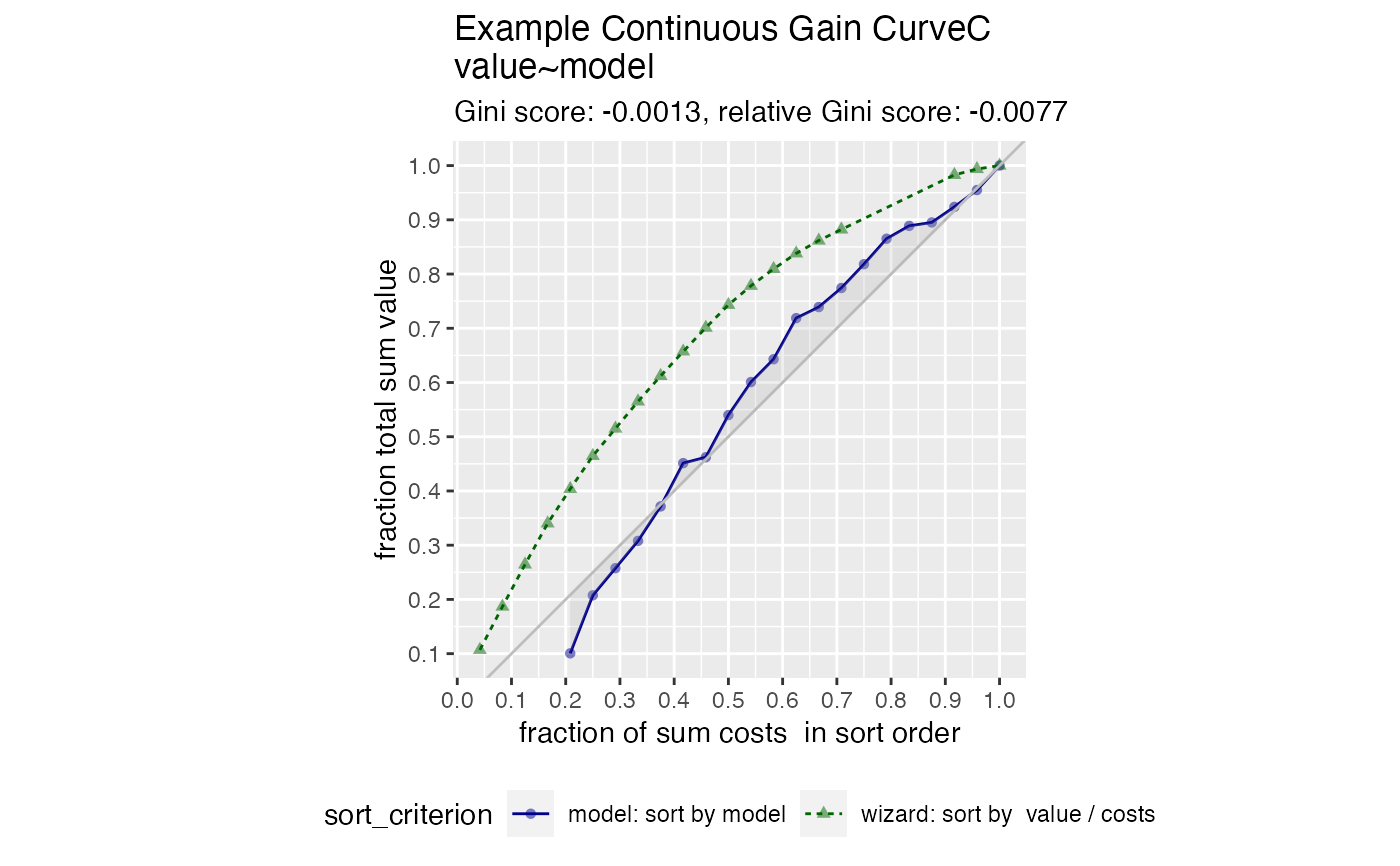
Plot the cumulative gain curve of a sort-order with costs.
GainCurvePlotC( frame, xvar, costVar, truthVar, title, ..., estimate_sig = FALSE, large_count = 1000, model_color = "darkblue", wizard_color = "darkgreen", shadow_color = "darkgray" )
Arguments
| frame | data frame to get values from |
|---|---|
| xvar | name of the independent (input or model score) column in frame |
| costVar | cost of each item (drives x-axis sum) |
| truthVar | name of the dependent (output or result to be modeled) column in frame |
| title | title to place on plot |
| ... | no unnamed argument, added to force named binding of later arguments. |
| estimate_sig | logical, if TRUE compute significance |
| large_count | numeric, upper bound target for number of plotting points |
| model_color | color for the model curve |
| wizard_color | color for the "wizard" (best possible) curve |
| shadow_color | color for the shaded area under the curve |
Details
GainCurvePlotC plots a cumulative gain curve for the case where
items have an additional cost, in addition to an outcome value.
The x-axis represents the fraction of total cost experienced when items are sorted by score, and the y-axis represents the cumulative summed true outcome represented by the items seen so far.
For comparison, GainCurvePlotC also plots the "wizard curve": the gain curve when the
data is sorted according to its true outcome/cost (the optimal sort order).
To improve presentation quality, the plot is limited to approximately large_count points (default: 1000).
For larger data sets, the data is appropriately randomly sampled down before plotting.
See also
Examples
set.seed(34903490) y = abs(rnorm(20)) + 0.1 x = abs(y + 0.5*rnorm(20)) frm = data.frame(model=x, value=y) frm$costs=1 frm$costs[1]=5 WVPlots::GainCurvePlotC(frm, "model", "costs", "value", title="Example Continuous Gain CurveC")